AdaptVision is an open-source model that leverages agentic visual tool use for dynamic visual token reduction, achieving a sota-level accuracy-efficiency trade-off across multiple VQA benchmarks.
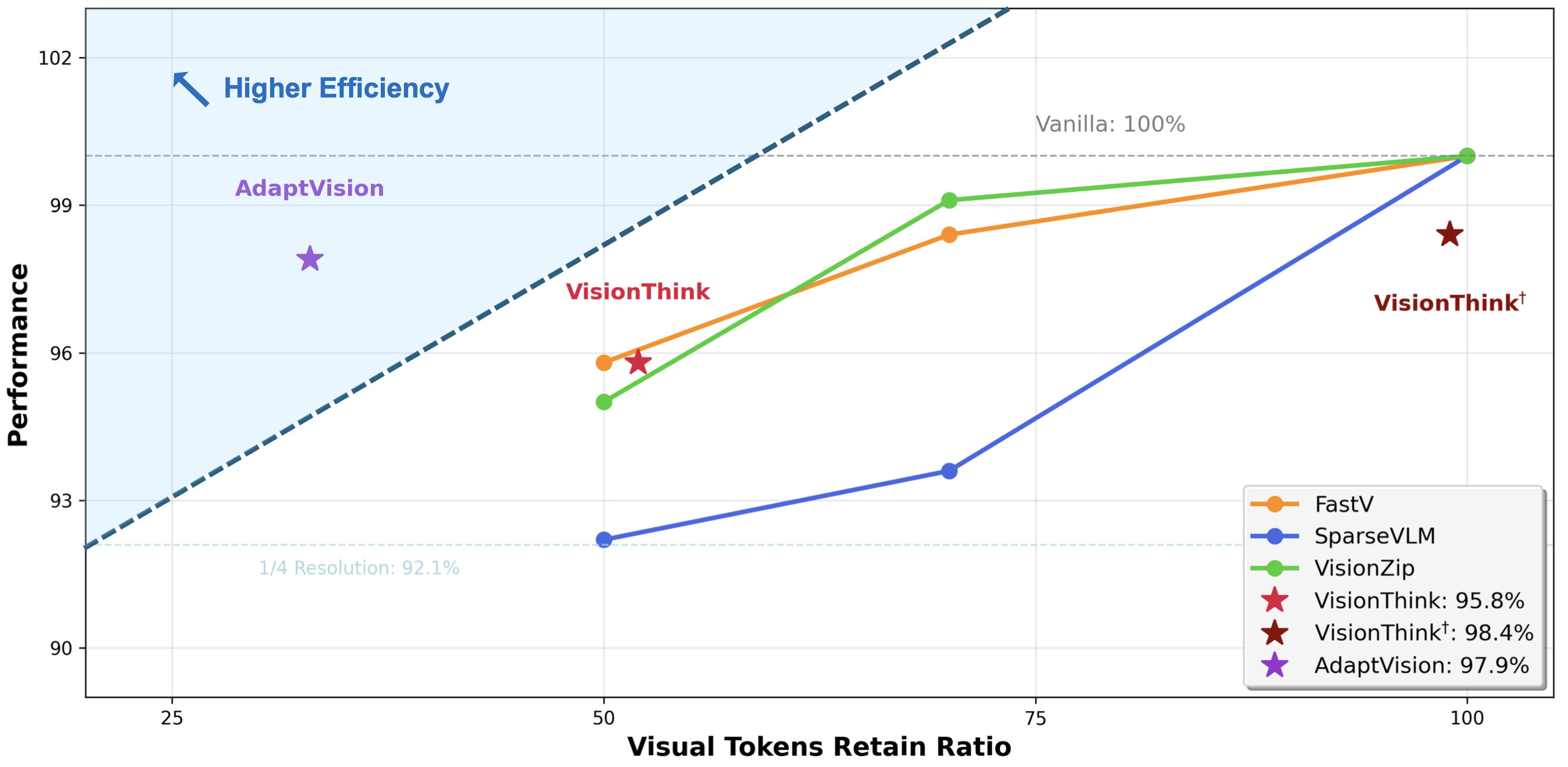
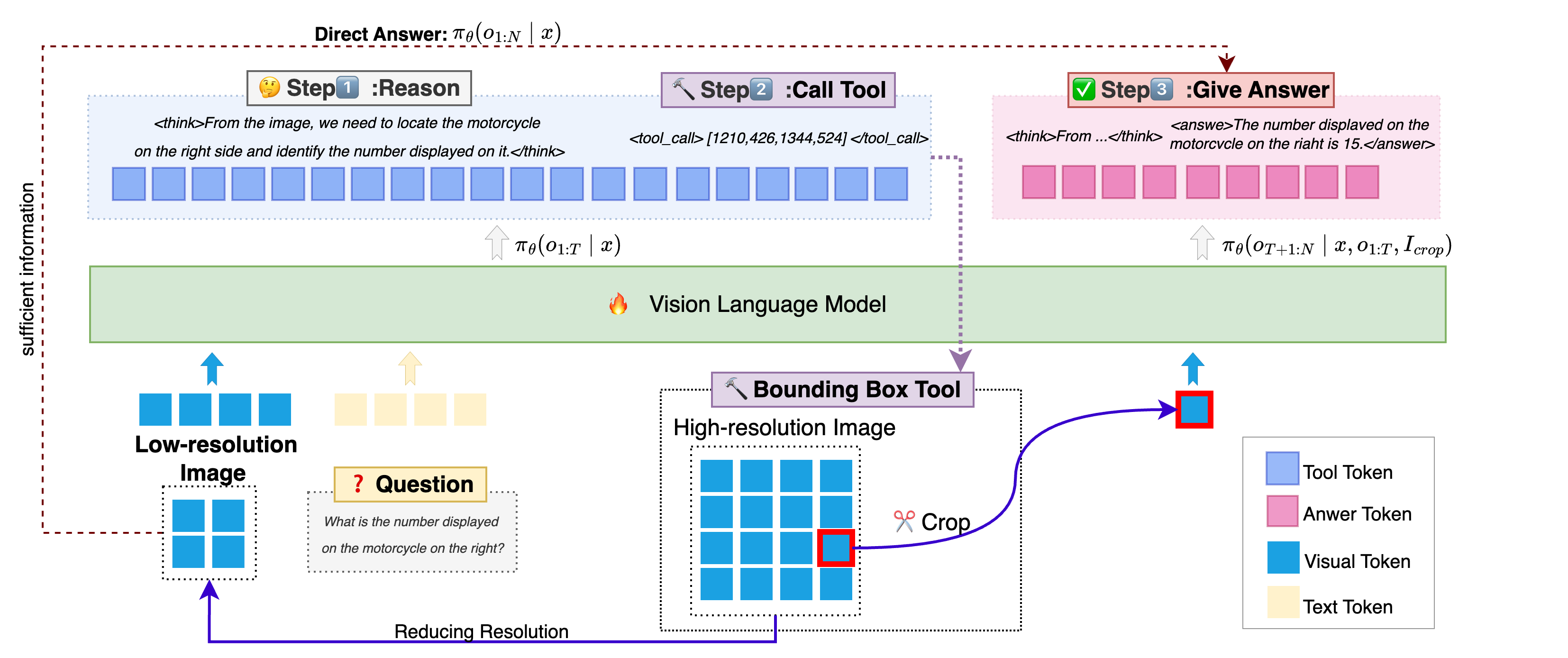
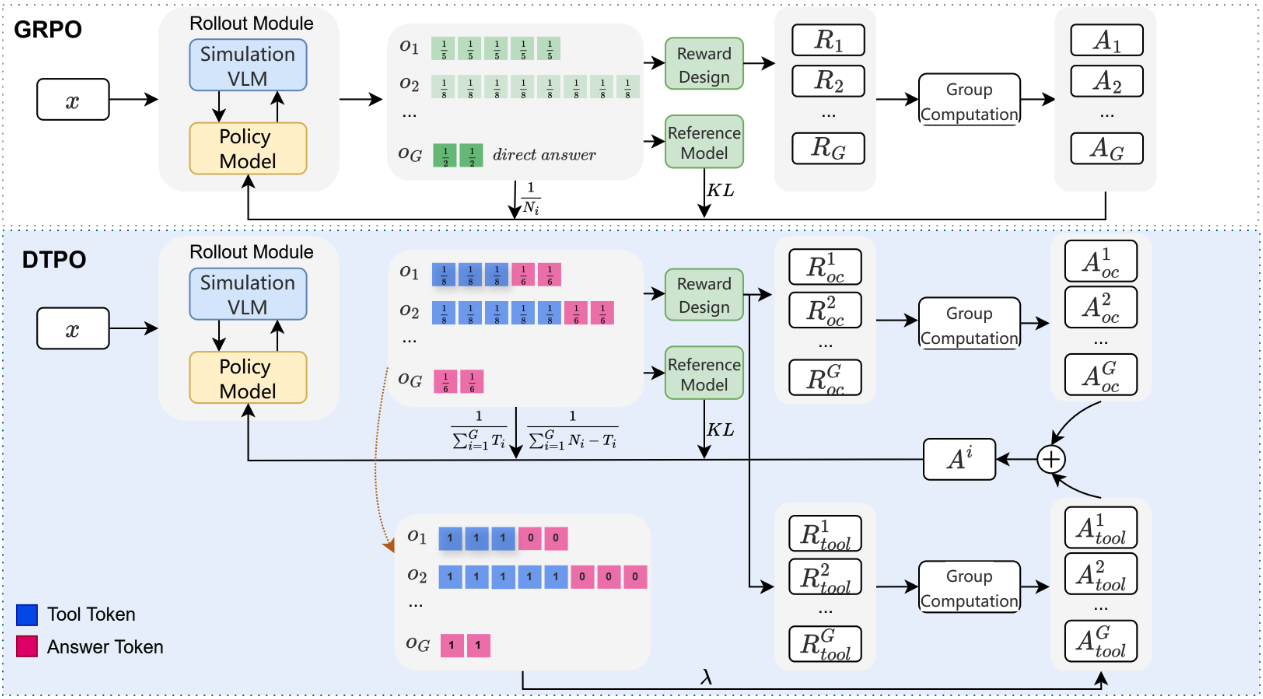
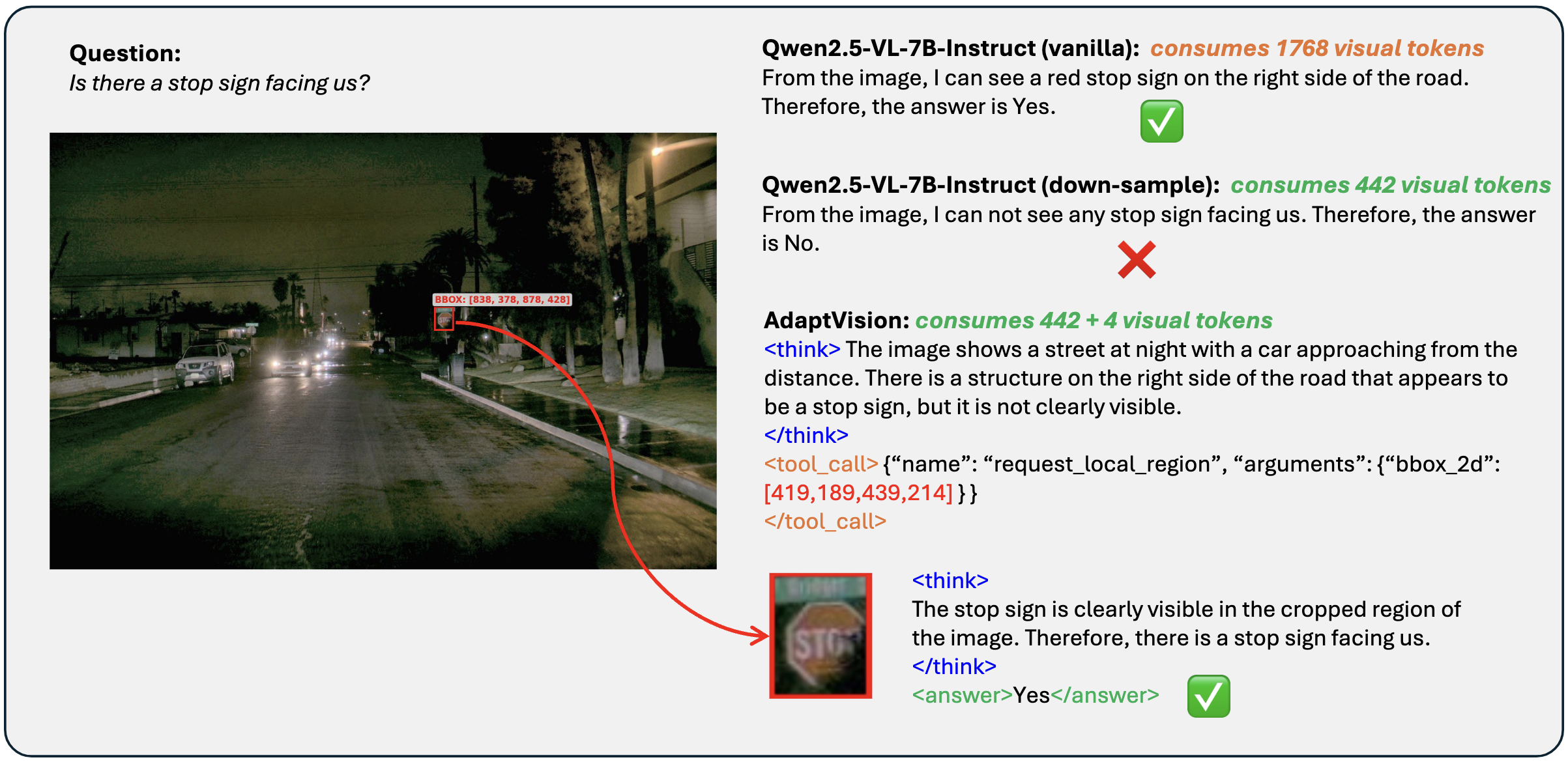
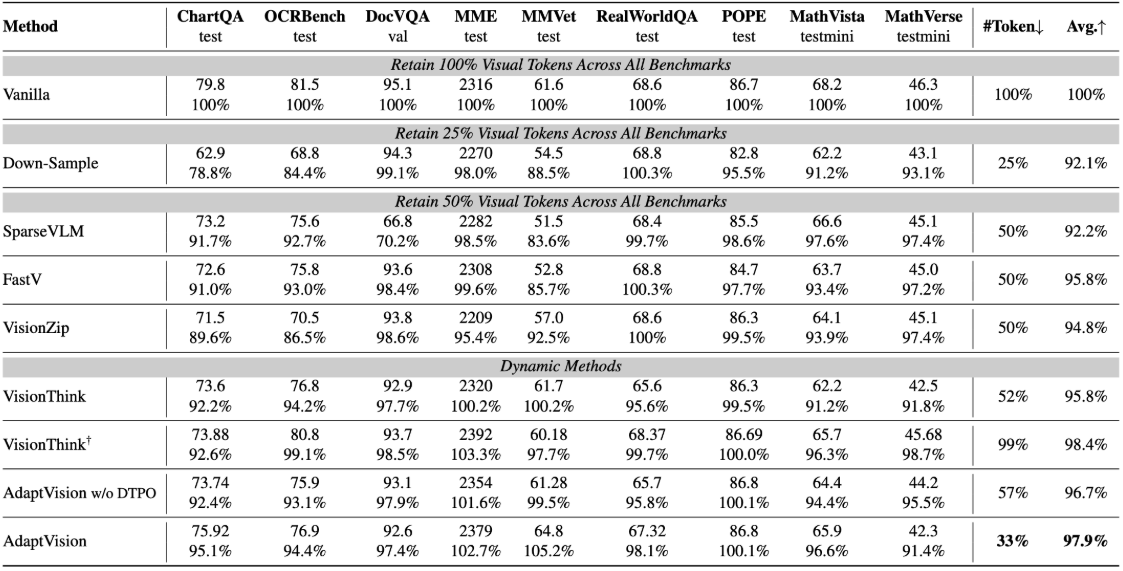
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable success in visual question answering tasks, but their reliance on large numbers of visual tokens introduces significant computational overhead. While existing efficient VLM approaches reduce visual tokens through fixed-ratio compression, they operate passively and lack the ability to adapt to varying task requirements. This motivates a fundamental question: Can VLMs autonomously determine the minimum number of visual tokens required for each sample? Inspired by human active vision mechanisms, we introduce AdaptVision, an efficient VLM paradigm that enables adaptive visual token acquisition through a coarse-to-fine approach. Our model initially processes compressed visual tokens from low-resolution images and selectively acquires additional visual information by invoking a bounding box tool to crop key regions when necessary. We train AdaptVision using a reinforcement learning framework that carefully balances accuracy and efficiency. Central to our approach is Decoupled Turn Policy Optimization (DTPO), which decouples the learning objective into two components: (1) tool learning, which optimizes correct tool utilization, and (2) accuracy improvement, which refines the generated responses to improve answer correctness. Based on this formulation, we further decouple advantage estimation by computing separate advantages for tokens associated with each objective. This formulation enables more effective optimization for AdaptVision compared to vanilla GRPO. Comprehensive experiments across multiple VQA benchmarks demonstrate that AdaptVision achieves superior performance while consuming substantially fewer visual tokens than state-of-the-art efficient VLM methods.
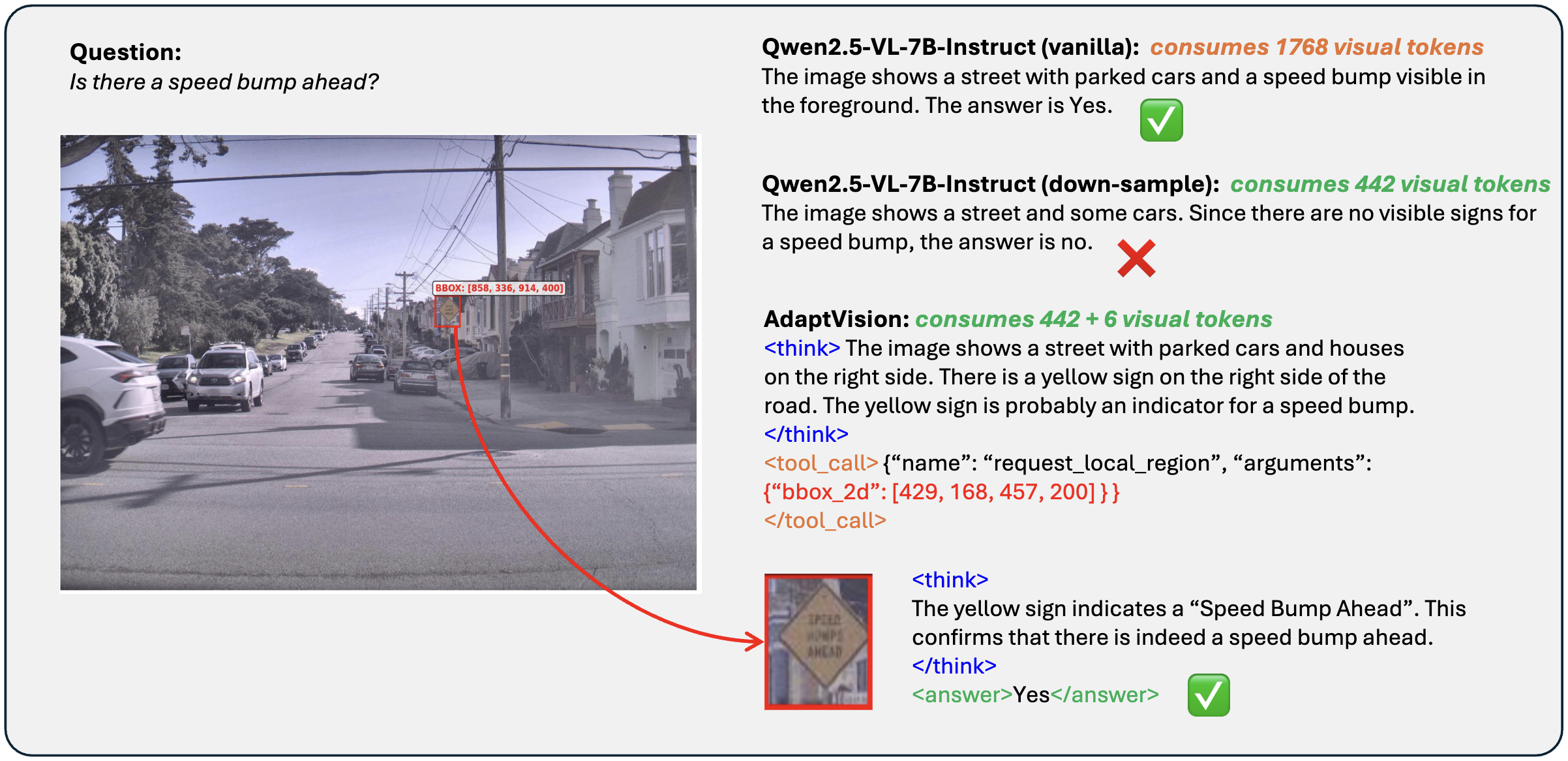
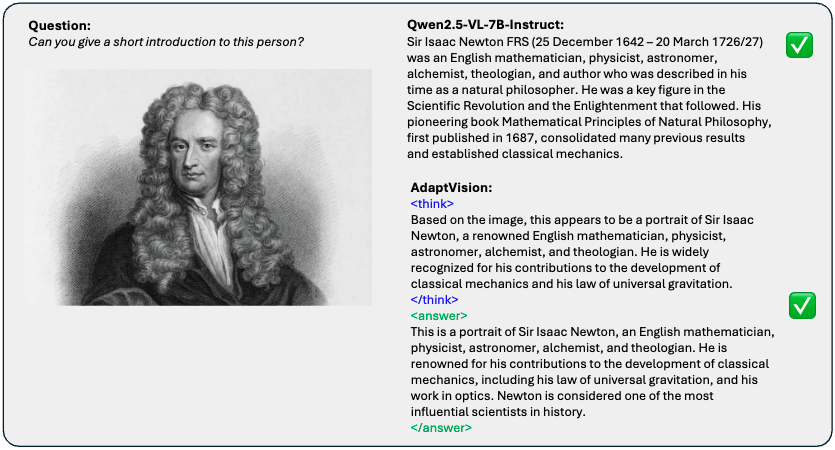
 Demo
Demo

This website is adapted from Nerfies, LLaVA and Mini-o3, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. We thank the Qwen team for giving us access to their models, and open-source projects including VisionThink.
Usage and License Notices: The data, code and checkpoint is intended and licensed for research use only. They are also restricted to uses that follow the license agreement of Qwen and Gemini-2.5-Pro. The dataset is CC BY NC 4.0 (allowing only non-commercial use) and models trained using the dataset should not be used outside of research purposes.